By Sanjay Verma
| May 22, 2020 | In
Articles
| Update: Jun 14, 2020
| Total Views [ 4928 ]
About NSX
- No physical component required
- Non-Disruptive process
- Provide distributed services
- Network Abstraction (VXLAN)
- Provides Automation for Networking services
- Provides distributed logical routing
- Provide Edge services such as (NAT, DHCP, IPSEC, VPN, NLB)
- Provides distributed firewalling
- Provides micro-segmentation
- Integration of 3rd party extension
- Resource Intensive
What is NSX-V?
NSX-V refers to a specialized software-defined networking solution offered by VMware. Its main function is to provide virtualized networking to software defined datacenter(SDDC). It enables the virtual cloud network, a software-defined approach to networking that extends across data centers, clouds, and application frameworks. With NSX-V, networking and security are brought closer to the application wherever it’s running, from virtual machines (VMs) to containers to bare metal. Like the operational model of VMs, networks can be provisioned and managed independent of underlying hardware. NSX-V reproduces the entire network model in software, enabling any network topology—from simple to complex multitier networks—to be created and provisioned in seconds.
Benefits of NSX-V
- Micro-segmentation
- Multi-Cloud Networking
- Network Automation
- Cloud-Native Apps
Why should we deploy NSX?
Network Abstraction
- Extend L2 Network
- Provide Micro-segmentation
- Provide VXLAN encapsulation
Edge Services
- Firewall
- NAT
- Routing
- DHCP
- NLB
- IPSec VPN
- VPN
- SSL Offload
Distributed Firewall and Routing
- Apply firewall and routing policies on hosts.
- Allows micro-segmentations
- Efficient Firewalling
Automation
- Ability to define and apply policies through automation
3rd Party Extensions
- Flexibility to additional services
- IDS/IPS Services
- Anti-malware
- Layer 7 firewalling
- No agent required
- Lower resource utilization
Common Use Cases of NSX
- Security
- Compliance
- Time for Provisioning
- Automation in Networking Services
- Same subnet of DR in production and recovery site. Same IP can be used at both side.
- Micro-segmentation helps to reduce uses of malware softwares at each client machine.
- Maximized hardware sharing across tenants (and physical sites).
- IT Automation
- Deployment of Cloud
- Multitenant Infrastructure
- Micro-Segmentation
- DMZ Anywhere
- Secure End User
- Disaster Recovery
- Metro Pooling
- Hybrid cloud Networking
- NSX enables a Zero-Trust security model
- Security by Design
- Minimized Risk
- Full visibility and Context
- Third-Party Integration
- Regulatory Compliance
Licenses of NSX
- Standard Edition
- Network agility and automation
- Advanced Edition
- Supports Micro-segmentation
- Standard Edition plus a fundamentally more secure data
- Enterprise Edition
- Supports Cross vCenter
- Advanced edition plus networking and security across multiple domains.
- Remote Branch Office Edition
- Automates and secures workloads in remote or branch offices.
NSX Components
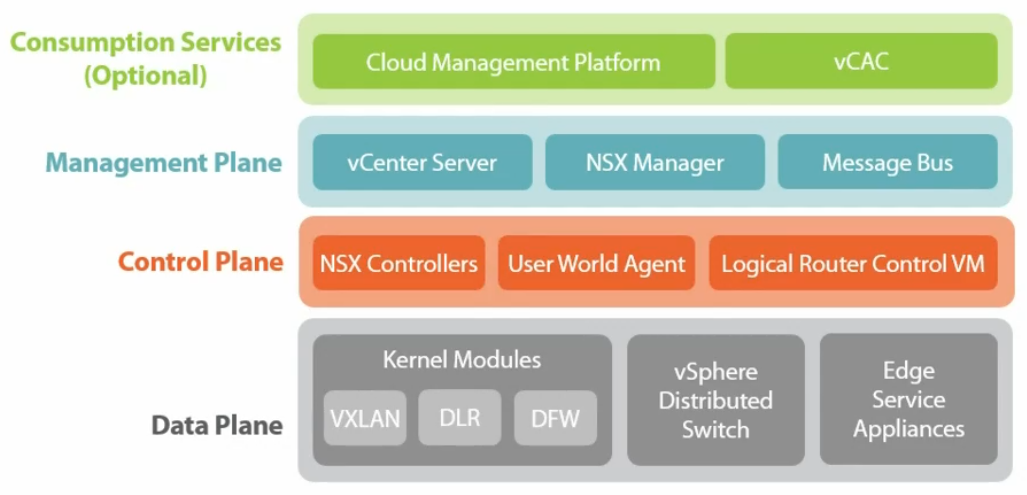
Management Plane
- Act as a management interface.
- Receive instruction from vCenter, Cloud Platforms, and RESTful API
- Deployed as a Virtual Appliance
- No impact on VM communications if NSX manager is down.
- 4 vCPU/12 GB RAM/ 60GB HDD
- Responsible to provide VXLAN on Logical routers.
- Routing information is also giving
- They are clustered. Network information is sliced across different NSX controllers. If one NSX controller will take care of one DLR then one controller will take care of logical switch, third one will take care of another logical switch.
- Maintain 4 tables (3 switching (ARP, MAC, VTEP) and 1 routing)
- Control plane for NSX
- Deployed in cluster arrangement – in Odd Number (Usually 3)
- Provide VXLAN directory service (MAC, ARP, VTEP)
- Remove dependency on multicast for VXLAN functionality
- Deployed by NSX management console
- Required 3 IP addresses for NSX Controller (If 3 controllers)
- 4 vCPU/ 4GB
- Logical Switch (VXLAN)
- DLR
- Firewall
- DLR Control VM (Appliance)
Data Plane
- Hypervisor Kernel Modules
- Logical Switch (VXLAN)
- DLR
- Firewall
- NSX Edge (Appliance)
- ESXi Host
- dvSwitch
VMware NSX & Cloud Computing SME | I am vExpert 2018 | VCP5-DCV, VCA Cloud, CCNA, MCSE, ITIL | AWSCSA | MSAzure